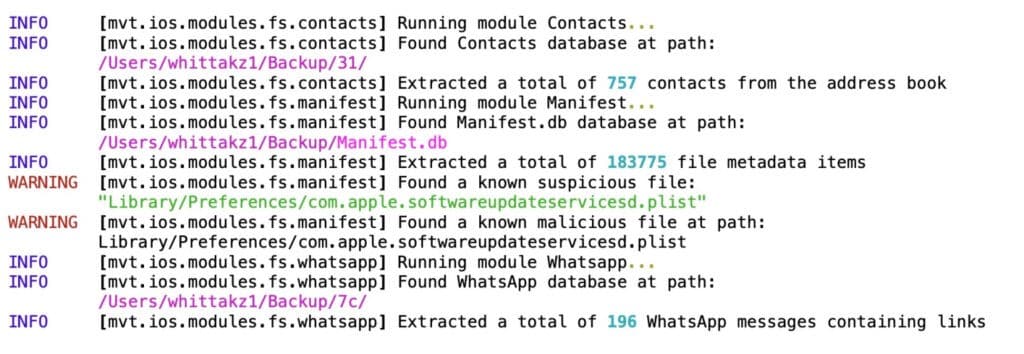
Forensic Analysis of NSO Group Pegasus
January 24, 2023
What is Cell Phone Forensics?
January 24, 2023Forensics and eDiscovery are two distinct disciplines with different skillsets, but clients sometimes have trouble distinguishing between them. According to a federal judge, eDiscovery involves navigating to files on a computer as a user, while Forensics involves using specialized software, recovering data, examining deleted data, or interpreting complex files. Wholesale data collection can be challenging due to the various storage and media types in modern systems, such as RAID storage, encrypted drives, MacBooks, mobile phones, and vehicle infotainment systems. There is various types of data that can be preserved and each may often require different software tools to preserve the files and the metadata.
Data preservation is crucial in both Forensics and eDiscovery, but the methods and extent of preservation can differ. Some basic preservation methods include Copy and Paste, Zip and Copy, Targeted Collection, Logical Collections, Physical Imaging, and Device Storage. However, it is important to note that none of the above methods will capture deleted data.
The costs of each preservation method vary, and it is essential to consider the type of preservation, as well as the potential costs of overcollection during the culling process.
How you preserve data greatly affects your case!
CALL GARRETT DISCOVERY
None of the methods below will capture deleted data!
Most forensic and eDiscovery professionals are familiar with data preservation. We often see eDiscovery professionals wanting to only preserve what is relevant and necessary and forensic professionals wanting to preserve everything. It is important to understand the types of preservation and what is preserved when choosing that method. A few basic types are:
Copy and Paste – End users usually do this if they have to produce a single document and this may be appropriate in some circumstances, it is certainly not a sound practice.
Zip and Copy – This will preserve the file metadata and file properties. This is useful if you only have a handful of items to preserve.
Targeted Collection – Usually a data preservation tool can be installed on the computing device and a selection of files and folders is made to preserve. This is forensically sound if using software that is generally accepted by the community.
Logical Collections – Can be the same as #3 above or you can select an entire logical partition of a hard drive (C:\, D:\ etc.).
Preserve data immediately to avoid spoliation issues.
CALL GARRETT DISCOVERY
The methods below will capture deleted data!
Physical Imaging – This created a true copy of a physical device such as an entire hard drive. This is the most complete forensic method and is used when deleted data is needed or there is a good faith claim of spoliation.
Device Storage – Storing a device for safekeeping and later being able to use one of the methods below is sound as long as the device doesn’t have a chance of data loss due to not being connected to power.
If you are seeking assistance in your legal matter either with digital forensics or electronic discovery call Garrett Discovery at 888.822.5077.

